In the world of thermal management, the aluminium heat exchanger stands out as a prime example of intelligent engineering. As modern industries demand better heat dissipation, energy efficiency, and compact designs, aluminium heat exchangers have emerged as a smart combination of advanced materials, innovative manufacturing, and multi-industry application.
Whether used in automotive, HVAC, industrial equipment, or renewable energy systems, aluminium heat exchangers offer a unique blend of benefits that traditional systems struggle to match. This article explores how the integration of aluminium’s properties with smart design principles makes these heat exchangers a vital component in today’s thermal solutions.
Unlike copper or stainless-steel variants, aluminium heat exchangers capitalize on aluminium’s natural advantages: excellent thermal conductivity, light weight, corrosion resistance, and formability. This combination allows for optimized heat performance in a compact, durable design.
Aluminium offers a unique combination of physical and chemical properties ideal for heat exchanger applications:
High thermal conductivity: With conductivity around 205 W/m·K, aluminium transfers heat quickly and efficiently.
Low density: It is about one-third the weight of steel or copper, reducing the overall mass of the system.
Corrosion resistance: A naturally forming oxide layer protects aluminium in most environments.
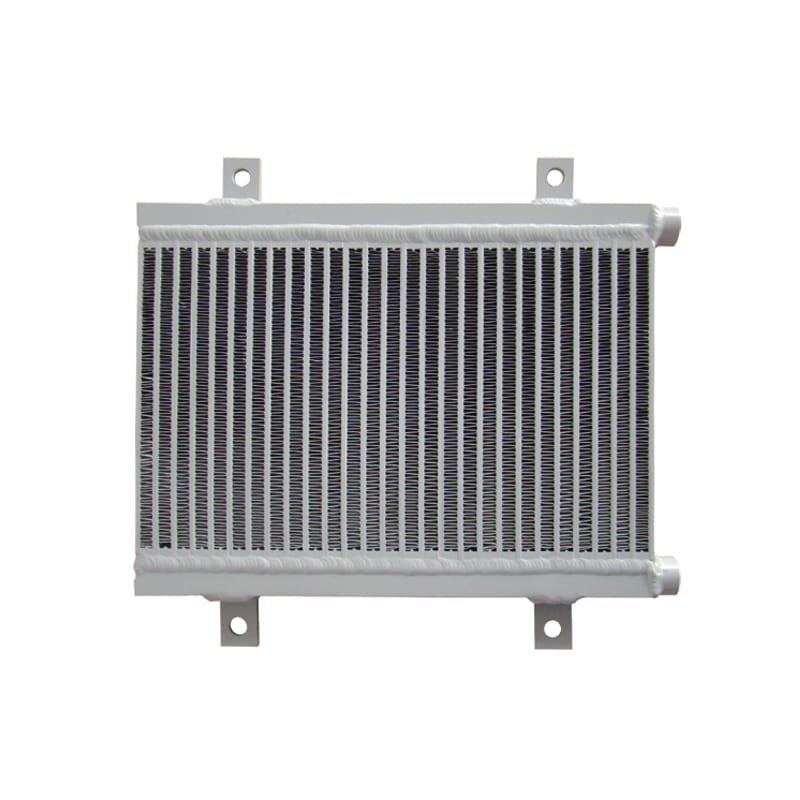
Easy formability: Aluminium can be extruded, stamped, or bent into intricate shapes, enabling highly efficient fin and tube designs.
Cost-effective: Aluminium is more affordable and sustainable, particularly in large-scale applications.
The combination of these traits enables the production of heat exchangers that are not only efficient but also affordable, durable, and easier to handle and install.
The effectiveness of an aluminium heat exchanger doesn’t come from the material alone—it’s the combination of material science and smart engineering. Manufacturers have developed compact microchannel or plate-fin designs that significantly increase the surface area, improve airflow, and reduce pressure drops.
Additionally, modern heat exchangers are often integrated directly into larger mechanical or electronic systems. For example, in electric vehicles, aluminium heat exchangers are combined with battery cooling systems to maintain optimal performance. In air conditioners, they are integrated into the evaporator and condenser units for efficient thermal cycling.
This combination of advanced design with precise thermal control is key to achieving energy savings and long-lasting performance.
The versatility of aluminium heat exchangers is demonstrated by their widespread use:
Automotive industry: Used in radiators, intercoolers, and oil coolers due to their light weight and efficient heat transfer.
HVAC systems: Incorporated into residential and commercial heating/cooling units for improved energy performance.
Industrial machinery: Help maintain temperature control in compressors, welding machines, and process equipment.
Renewable energy: Support cooling in solar inverters, wind turbines, and energy storage systems.
Aerospace and marine: The weight-saving benefits of aluminium are critical in weight-sensitive applications.
Each use case showcases a tailored combination of aluminium’s strengths with design features optimized for specific thermal challenges.
Another important advantage of aluminium heat exchangers is their environmental benefit. Aluminium is 100% recyclable without loss of quality, making these exchangers an eco-friendly solution. Recycled aluminium consumes up to 95% less energy than primary production, contributing to carbon footprint reduction.
By combining performance with sustainability, aluminium heat exchangers align with global trends in green engineering and circular economies.
While aluminium heat exchangers offer many advantages, they are not without challenges. Aluminium is softer than copper or steel, making it more susceptible to damage if not properly handled. However, ongoing innovations in protective coatings, welding techniques, and composite materials are addressing these concerns.
The future lies in combining aluminium with other technologies—such as nanocoatings, phase-change materials, and smart temperature sensors—to create next-generation heat exchange systems that are even more intelligent and efficient.

 English
English русский
русский












